If you're diving into Java development, understanding the roles of JDK, JRE, and JVM is essential. These three components form the foundation of Java’s “Write Once, Run Anywhere” philosophy. Here’s a quick and clear breakdown to help you revise fast.
🔹 What is JVM?
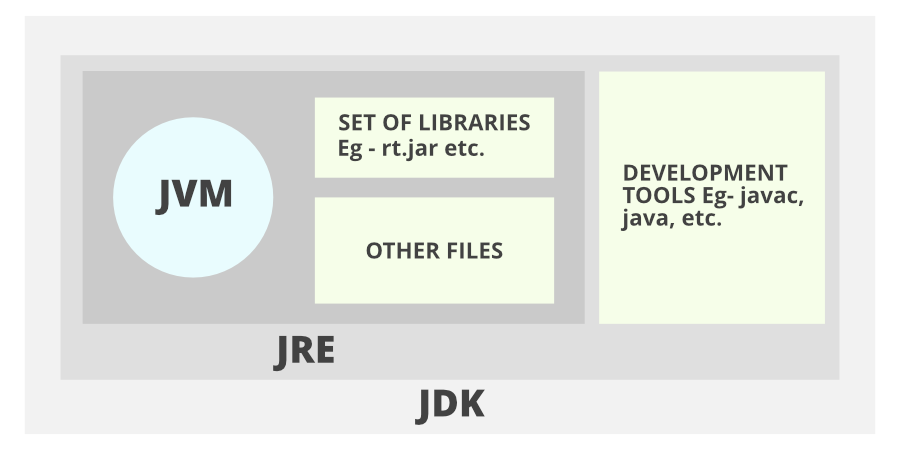
JVM (Java Virtual Machine) is the engine that actually runs Java programs. When you compile Java code, it gets converted into bytecode (.class files). JVM interprets this bytecode and executes it on your machine.
✅ Key Responsibilities of JVM:
- Loads class files
- Verifies bytecode
- Executes bytecode
- Handles memory management and garbage collection
📝Think of JVM as the executor of your compiled Java code.
🔹 What is JRE?
JRE (Java Runtime Environment) is the package that provides the environment required to run Java programs. It includes:
- The JVM
- Core Java libraries
- Supporting files and configuration
📝If you only want to run Java apps (not develop), JRE is enough.
🔹 What is JDK?
JDK (Java Development Kit) is the full-featured software development kit for Java. It includes:
- JRE (and hence JVM)
- Java compiler (
javac) - Development tools (debugger, documentation tool, etc.)
📝If you want to write and compile Java programs, you need the JDK.
🔄 Summary Table
| Feature | JVM | JRE | JDK |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Executes Java bytecode | Provides runtime environment | Provides tools to develop Java apps |
| Includes | - | JVM + Libraries | JRE + Compiler + Dev Tools |
| Used by | Users and developers | Users | Developers |
| Contains Compiler | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ |
| Can Run Java Code | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Can Compile Java Code | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ |
🎯 Final Thoughts
- JVM is the core engine.
- JRE = JVM + Libraries (to run Java).
- JDK = JRE + Compiler/Tools (to develop Java).
🚀So, if you're building Java apps — get the JDK. If you're just running them — the JRE will do!

Comments
Post a Comment